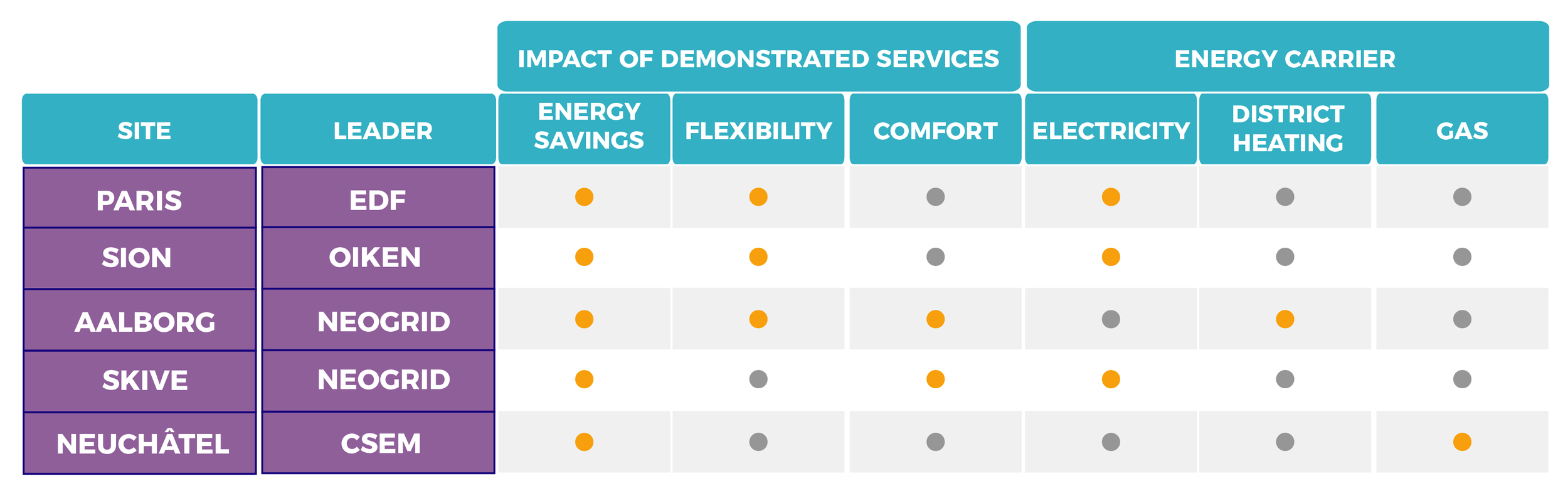
DEMONSTRATORS
Demonstrators play a key role in domOS: their requirements drove the design of the domOS ecosystem, and they host domOS compliant IoT platforms.
Each demonstrated service brings its own contribution to more energy-efficient, more flexible and more prosumer-friendly energy systems. The domOS ecosystem aims at simplifying their development and deployment in the context of buildings equipped with various appliances and devices.
Sion, Switzerland
Sion is a mid-size Swiss city located in the centre of the Alps. It is surrounded by big hydro reservoir power plants, and its sunny climate makes it an ideal place for hosting photovoltaic installations.
In the domOS demonstrator, the installed in-building infrastructure is made available to a cluster of services for prosumer empowerment, flexibility control and data services.
OIKEN is able to control the flexibility of participating heat pumps to decrease the gap between the day-ahead energy schedules and the effective production/consumption (balance energy reduction).
Demonstrator highlight
Demonstration site leader
OIKEN is a multi-fluid energy provider for the Central Valais region in Switzerland. For electricity, OIKEN acts as energy provider, metering operator, distributor (DSO), public EV charging station operator, and producer.
Participating partners
In-building infrastructure
The infrastructure deployed in a building of the Sion demonstrator.
The following devices are connected to a building gateway: smart meter, submeters for the heat pump, the charging station, and the solar inverter, ambient temperature sensor, sensor for the domestic hot water tank, enable/disable relay for heat pumps.
Demonstrated services
Disaggregation of an electrical load curve, to be used for the energy dashboard service.
A cluster of energy services related to electricity are demonstrated: energy dashboard for prosumers, flexibility management for space heating and domestic hot water preparation, and smart metering for the DSO and the suppliers.
Supporting IoT platform
Neuchatel, Switzerland
Neuchatel is an average-sized Swiss city of around 33 thousand inhabitants. The city is close to the lake of Neuchatel and the mountains of the Jura. It has a degraded oceanic climate, with cold winters and warm summers.
In the domOS demonstrator, the objective was to reduce (space) heating expenditure by using a novel heat generation algorithm.
Demonstrator highlight
The demonstrator allowed validation of the proposed concept as we could demonstrate a forward temperature decrease of -2 to -5°C per riser, this translated into a valve opening increase of +5 to +20%. Unfortunately, the tests highlighted that the heat generator is greatly over-dimensioned, in consequence, the benefits observed at the riser level could not be tracked back to the heat generator in terms of primary energy savings.
Demonstration site leader
CSEM is a research and development centre with headquarters in Neuchatel. With historical roots in the watch industry, CSEM has now a strong focus also on renewable energy: PV, batteries and energy management in general.
In-building infrastructure
Neuchatel demonstrator architecture. The following devices are connected to smart gateways:
Smart thermostatic (radiator) valves
Heat generator (gas boiler)
The sensor data is sent to a DB centralized at CSEM where the processing of the optimal heating set-point is performed.
Demonstrated services
Forward temperature decrease in one of the heating circuit (left) and increased valve opening (right).
The closed loop energy service was demonstrated on the Neuchâtel site.
Supporting IoT platform
Paris, France
In the Paris demonstrator, the installed in-building infrastructure is made available to a cluster of services for prosumer empowerment, energy coaching and a no-energy service to help elderly people.
The EDF platform and the overall IoT infrastructure with a gateway and new smart meter collect the global electrical load curve every 5 seconds. This solution has been designed to comply with the EDF security policy. With this new IoT platform, EDF can now deploy any services on this platform.
Demonstrator highlight
Demonstration site leader
EDF is a multi-fluid energy provider for France. With 90% of its electricity carbon-free, EDF plays a leading role in the construction of a net zero energy future. The aim is to create new solutions for saving energy and decarbonising energy use.
In-building infrastructure
The infrastructure deployed in a building of the Paris demonstrator
EDF platform is a scalable open-source IoT (Internet of Things) platform developed by EDF-Lab and based on the deployment of a containerised docker application. The platform operates gateways deployed on the premises of households. A ZigBee coordinator is embedded in the gateways and manages an ecosystem of end devices. The gateways communicate with the EDF platform via the participant's wifi router.
Demonstrated services
IoT Monitoring & Control (with a gateway and the ERL smart meters)
The first service is the connected building called the datalogger. It allows the control of connected objects. The services are managed on a home automation platform. The user can interact via a mobile application available now. The second service is energy coaching to reduce energy consumption. The third service is energy coaching for flexibility. Finally, we also present a non-energy service to help the frail.
Aalborg Living Lab, Denmark
Kildeparken is a residential area on the east side of Aalborg that has undergone a low-carbon refurbishment. The 54-hectare area is comprised primarily of buildings (two-storey multi-family apartments and single-family houses) and green areas and has approximately 2 450 inhabitants. The buildings in Kildeparken were constructed in the 1970s, and those to be used for the Aalborg demonstrator in the domOS project, have been refurbished to energy class B and have smart meters installed. All the buildings are heated by district heating, where the water is mixed down to a lower temperature, and distributed to the apartments.
Infrastructure
AFE has installed a mixing loop at the supply to a sub-area consisting of 12 multi-family buildings (144 apartments), where we have the possibility to control the temperature of the whole area. The buildings are owned by Himmerland Housing Association (HB), an association all residents are members of.
BMS substations are installed in each building, controlling space heating and domestic hot water production. All the substations are managed by a BMS Main Station, where NEOGRID via BMS protocols interact with all the buildings. A percentage of the apartments are equipped with multi-sensors measuring temperature and relative humidity.
Web of Things access to devices
Arrowhead single cloud and its core services will host 2 essential services
Prototype service for energy control services
Use the ontology to describe buildings, installations (devices) and exchanged data
domOS compliant platform
Demonstrator highlight (old)
Demonstration site leader
Neogrid Technologies is an IT company providing solutions for energy efficiency and flexibility based on cloud-based heating control and energy management in buildings, as well as data collection from IoT devices and smart meters.
Participating partners
In-building and area of building infrastructure
AFE has installed a mixing loop at the supply to a sub-area consisting of 12 multi-family buildings (144 apartments), where we have the possibility to control the temperature of the whole area. The buildings are owned by Himmerland Housing Association (HB), an association all residents are members of.
Building controller, space heating
Demonstrated services
Space heating supply temperature
For each building, a controller continuously optimises the supply temperature delivered centrally to the space heating of the apartments. The control is based on 2 models:
An energy demand model, which forecasts how much energy will be used every hour in the coming hours, based on time and weather information.
A supply temperature limit model, which translates the energy demand forecast into a minimum supply temperature level.
District heating provider
Central mixing loop controller
Supply temperature control
Central mixing loop controller
Screenshot of building digital twin
Aalborg University has developed a digital twin of a one-family building. It consists of two primary:
a UI that shows the actual state of the building
thermodynamic models for simulation
The central mixing loop controller aims at minimising the supply temperature sent to the area, to minimise energy loss while ensuring that the district heating water received by the buildings is warm enough to allow their space and water heating to operate as required.
Supporting IoT platform
Demonstrator highlight (new)
2 essential services
Web of Things access to devices
Use the ontology to describe buildings, installations (devices) and exchanged data
domOS compliant platform deployed as Arrowhead single cloud
A prototype service for energy control
Heat pump Living Lab, Denmark
The heat pump Living Lab in Denmark is spread across 12 private households with existing heat pumps of various brands and models. Each of the houses has been upgraded with IoT devices that allow external control of the heating system.
Infrastructure
The different heat pumps are divided into 3 different categories:
Heat pump with MODBUS connection, controlled with a local gateway.
Heat pump without MODBUS connection, controlled via SG interface and temperature manipulation.
Heat pump with cloud connectivity and controlled via API interface.
The households cover 7 of the most popular brands on the Danish market. Each house has been fitted with Smart Thermostatic Valves and/or underfloor heating controllers with Modbus connectivity.
Web of Things access to devices
Arrowhead single cloud and its core services will host 2 essential services
Prototype service for energy control services
Use the ontology to describe buildings, installations (devices) and exchanged data
domOS compliant platform
Demonstrator highlights
Demonstration site leader
Neogrid Technologies is an IT company providing solutions for energy efficiency and flexibility based on cloud-based heating control and energy management in buildings, as well as data collection from IoT devices and smart meters.
Participating partners
Zone controller
Demonstrated services
The zone controller utilises predictive forecasting to achieve ideal comfort in different zones of the building.
Based on the IoT sensors throughout the building it will learn how different zones are influenced by external factors, such as solar and wind, as well as reaction time of radiators and underfloor heating.
Each zone will have its own comfort profile that the user can set as desired. It also includes profiles for weekends and vacation periods.
Price-optimized heat pump controller
Legacy heat pump controller
In order to be able to interface with ANY heat pump on the market – both existing and new installations, we have developed the NEOGRID Predator Gateway, which offers several different interface options.
Whenever possible MODBUS interface is available this is preferred, with the possibility to connect to the SG interface and/or temperature sensor manipulation.
The Predator gateway is low-cost and simple to install.
As the electricity prices fluctuate by the hour, it’s beneficial to control the heat pumps with a focus on both COPs (coefficient of production, and cost of production).
The price-optimized heat pump controller continuously monitors the cost of electricity and schedules the ideal production up to 36 hours in advance, while taking the specific heat demand into account.
Supporting IoT platform